- cross-posted to:
- askscience@lemmy.world
- til@lemmy.world
- cross-posted to:
- askscience@lemmy.world
- til@lemmy.world
cross-posted from: https://lemmy.world/post/6080744
The sun is not yellow or orange as we see in books and movies. It emits all the colours in the visible spectrum (also in other spectrums as well) making it white!


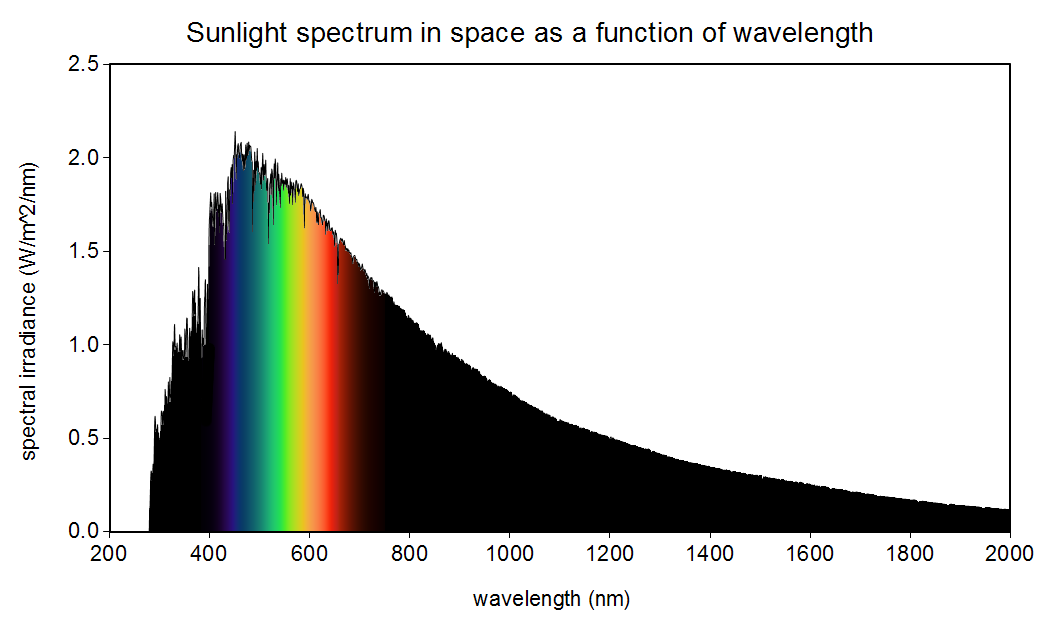
Am I missing something, or is the point about sunlight’s spectral peak being different in frequency space than wavelength space non-sensical?
Wavelength and frequency are simply the inverse of each other, and two different ways of describing the same color. The color with peak intensity is what it is, whether you describe it unsing wavelength or frequency.
Maybe the author meant some kind of integral / area under the curve concept, since the shape of the curve is different using wavelength vs frequency as the x axis, but even then, the actual power output across some spectrum range is independent of whether you define the range in terms of wavelength or frequency.
https://www.scielo.br/j/rbef/a/mYqvM4Qc3KLmmfFRqMbCzhB/?lang=en
This is something that bothered me when I was in undergrad but now I’ve come to understand. The article above goes through the math of computing different Wien peaks for different representations of the spectral energy density.
In short, the Wien peaks are different because what the density function measures in a given parametrization is different. In frequency space the function measures the energy radiated in a small interval [f, f + df] while in wavelength space it measure the energy radiated in an interval [λ, λ + dλ]. The function in these spaces will be different to account for the different amounts of energy radiated in these intervals, and as such the peaks are different too.
(I typed this on a phone kinda rushed so I could clarify it if you’d like)
Hey thanks for the reply! I’ll admit that paper lost me pretty quickly, so I am probably missing a subtle point. But it feels deeply unintuitive since frequency and wavelength are just two different ways of describing the same physical quantity.
So if I have a given source of photons, how the heck does the color of photons delivering most cumulative power change whether I choose to describe that color based on its wavelength or it’s frequency?
Is there an analogue to something like sound energy or is this quantum physics weirdness?
(These are semi rhetorical questions… I’m not expecting you to explain unless you really feel like it 😀)