- cross-posted to:
- space@lemmit.online
- cross-posted to:
- space@lemmit.online
Last week, NASA announced it is working with a technology development company on a new propulsion system that could transport humans to Mars in only two months – down from the current nine month journey required to reach the Red Planet. Gizmodo reports:
NASA’s Innovative Advanced Concepts (NIAC) program recently selected six promising projects for additional funding and development, allowing them to graduate to the second stage of development. The new “science fiction-like concepts,” as described by John Nelson, NIAC program executive at NASA, include a lunar railway system and fluid-based telescopes, as well as a pulsed plasma rocket.
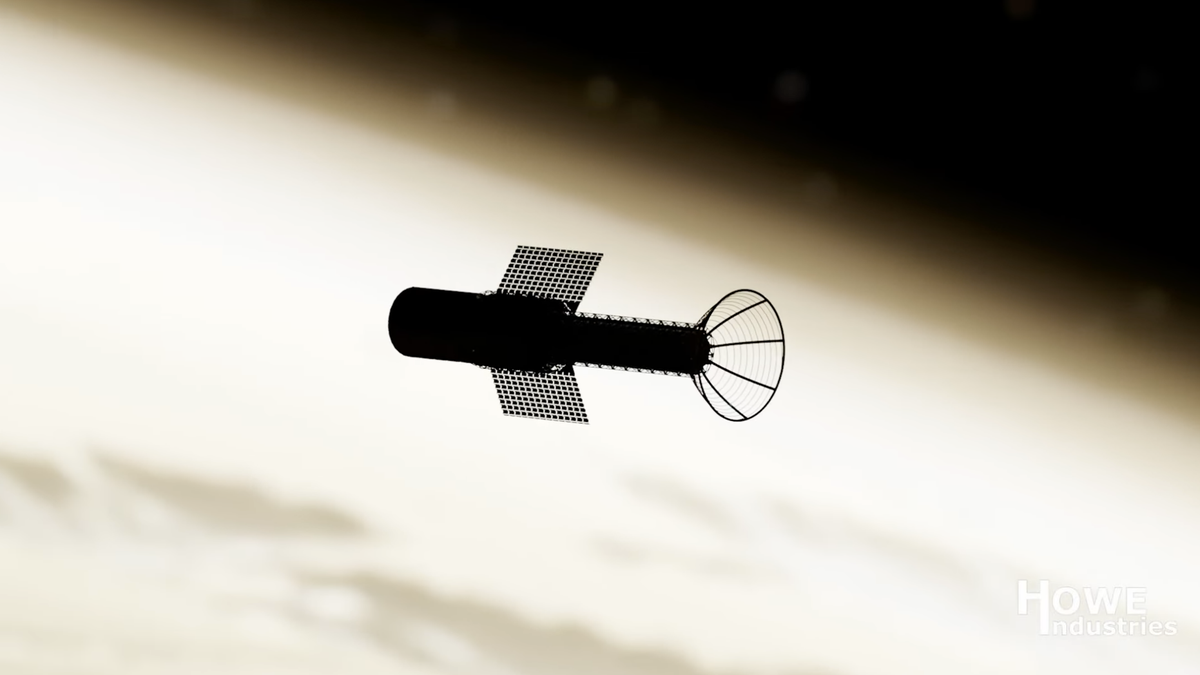
The potentially groundbreaking propulsion system is being developed by Arizona-based Howe Industries. To reach high velocities within a shorter period of time, the pulsed plasma rocket would use nuclear fission – the release of energy from atoms splitting apart – to generate packets of plasma for thrust. It would essentially produce a controlled jet of plasma to help propel the rocket through space. Using the new propulsion system, and in terms of thrust, the rocket could potentially generate up to 22,481 pounds of force (100,000 Newtons) with a specific impulse (Isp) of 5,000 seconds, for remarkably high fuel efficiency. […]
The pulsed plasma rocket would also be capable of carrying much heavier spacecraft, which can be then equipped with shielding against galactic cosmic rays for the crew on board. Phase 2 of NIAC is focused on assessing the neutronics of the system (how the motion of the spacecraft interacts with the plasma), designing the spacecraft, power system, and necessary subsystems, analyzing the magnetic nozzle capabilities, and determining trajectories and benefits of the pulsed plasma rocket, according to NASA.
Abstract credit: https://slashdot.org/story/428225


Maybe more like the drive that Solomon Epstein started with in the novella, The Drive, but with fission instead of fusion. I don’t think it would be any good for a manned ice-hauler trip out past the belt though as that would face the same problems that a trip to Mars currently faces.
On the other hand, if such a drive could get a crewed ship to Mars in two months then it should be able to reach the outer planets in a reasonable time with a much larger payload than we can manage now. We might well be able to send large robotic probes to the moons of Saturn and Jupiter like the ones we’ve sent to Mars and get there in months instead of years.